Risk Definitions
- Risk Appetite
- Most organisations tolerate a certain amount of Risk, balanced against the value gained from its activities where that Risk is a factor. For example, an aggressive Share Management organisation would likely balance a high tolerance for Risk against the potential returns on investment.
Risk Appetite indicates the level of Risk that an organisation is willing to tolerate. Every organisation has a different Risk Appetite. Influencing factors include:
- The Regulatory environment in which the organisation operates,
- Whether the organisational culture embraces risk or is risk-averse,
- Whether the expected outcomes from the organisation’s activities outweigh the Risks involved,
- Shareholders attitude to Risk, and
- The level of Risk that the Board is willing to embrace.
- In TriLine GRC, Risk Appetite is an optional feature that you can enable in the Risk Configuration settings. Once enabled, you can specify a Risk Appetite value for each Risk, and generate Risk Reports that show which Risks exceed your organisation’s Risk Appetite.
- Risk Matrix
- The Risk Matrix is accessed from the Risk Matrix icon. The Risk Matrix will highlight the Inherent and Residual Rating of the entity you are viewing the Risk Matrix from. The Legend highlights which Rating is which.
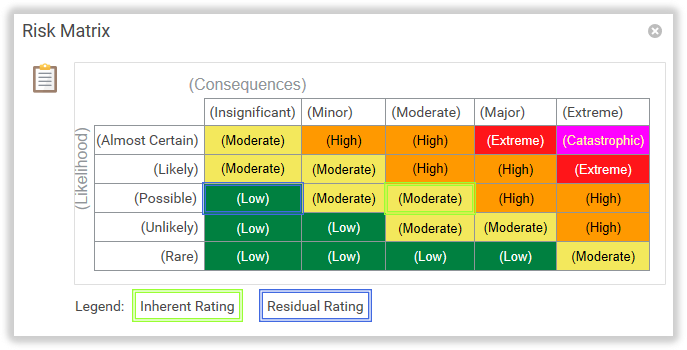
- Note: All labels in (Brackets) and all colours in the Risk Matrix are configurable and may be different in your TriLine GRC system.
- The Risk Matrix is a configurable 5 x 5 matrix that TriLine GRC uses to display a Risk Rating based on a Risk Assessment of Likelihood versus Consequences (or equivalent terms used by your organisation).
- Example of use
- Using the example Risk Matrix shown above, if you review a Risk and determine that the Risk has a Residual ‘Possible’ Likelihood of occurring with ‘Moderate’ Consequences, the Matrix returns a value of ‘Moderate’.
- Configuration
- The Risk Matrix is completely configurable to your organisation’s needs. You can set the colour and Rating for each combination of ‘Likelihood’ versus ‘Consequences’ by selecting Maintenance | Risk | Matrix from the Main Menu. You can also change the terms ‘Likelihood’ and ‘Consequences’ (and all labels within each,) if your organisation uses different terminology.
- Risk Matrix icon
- Click the icon to view the Risk Matrix.
- Risk Score Bands
Risk Scores are classified into Risk Score Bands determined by the values and colours set by the TriLine GRC Administrator. Example Risk Score Bands shown are:
- Negligible,
- Low (green),
- Moderate (yellow),
- High (orange), and
- Extreme (red).
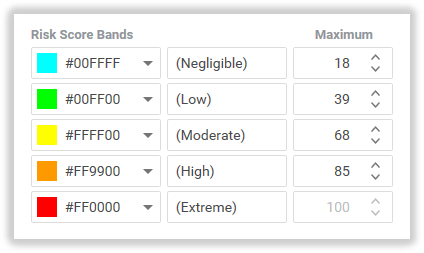
The exmaple above shows some sample Risk Score Band settings:
- Risk Scores from 0 to 18 will be classified in the ‘Negligible’ Band,
- Risk Scores from 18 to 39 will be classified in the ‘Low’ Band,
- Risk Scores from above 39 to 68 will be classified in the ‘Moderate’ Band,
- Risk Scores from above 68 to 85 will be classified in the ‘High’ Band; and
- Risk Scores above 85 will be classified in the ‘Extreme’ band.
- The Maximum (Extreme) value is locked to the maximum Risk Score Calculation.
- For each Risk, TriLine GRC displays Risk Scores and Risk Score Band information (colour and Band title) on the (Assessment) | Rating tab of the Risk Page and the Complete Risk Review Page.
- Risk Score Bands can be used as filters in Risk Reports and are also an optional column in Risk Lists.
- Risk Score Calculation
- Risk Score is related to the Risk Matrix—the ‘Likelihood’ and ‘Consequence’ components by default. TriLine GRC calculates and graphically displays the Risk Score on related Pages.
- Risk Scores are calculated by following a configurable mathematical formula involving—by default—‘Likelihood’ and ‘Consequence’ values. These values are also configurable. (See the example following.)
- A standard practice is to allocate a low score to the lowest Risk components (i.e. ‘Rare’ Likelihood and ‘Insignificant’ Consequences). For each subsequent higher Risk Rating, the value is increased, culminating in the highest Risk components (‘Almost Certain’ Likelihood and ‘Extreme’ Consequences) each attracting the highest score. (See the example below.)
- Calculation formula Example
- This exmaple calculation is set as:
Likelihood x Consequence = Risk Score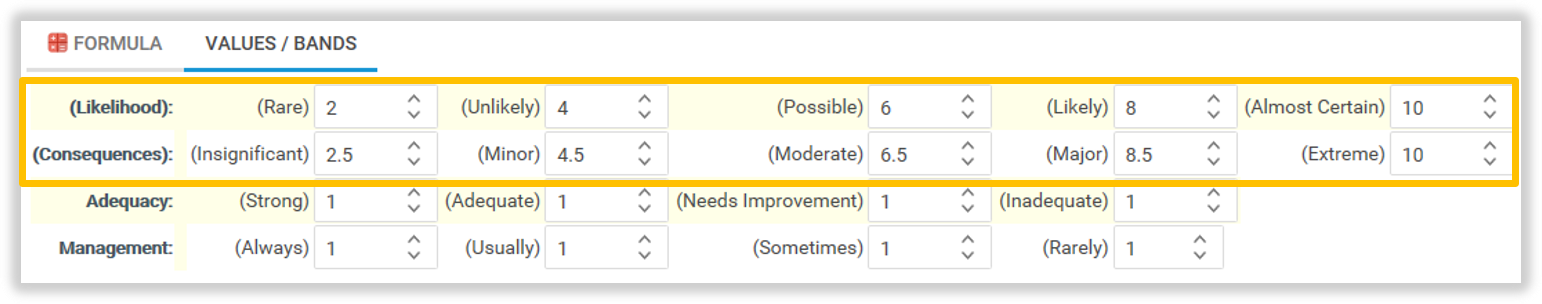
- Using the example ‘Likelihood’ and ‘Consequences’ Risk Rating values above, a Risk with a ‘Possible’ Likelihood (6) and ‘Minor’ Consequences (4.5) would result in a Risk Score of 27 (6 × 4.5).
- Note: Values for Adequacy and Management are also shown in the example screenshot above. In our calculation example, they will have no bearing on the Risk Score because our formula only includes ‘Likelihood’ and ‘Consequences’. However, you can edit the formula to include either or both Adequacy and Management values to refine the Risk Score.
- Configuration
- The example screenshot above shows values between the lowest and highest Risk Ratings in the range of 1 to 10. You can set these scores to whatever interval, or range you require.
- Availability of Risk Scoring options
- The Risk Scoring options must be enabled in the ‘Risk Assessment’ configuration settings in order to use the Risk Score Calculation feature.
Related Articles
Risk Module Configuration: General Risk Settings
The Drova GRC Configuration ‘Risk’ tab Establishing an appropriate Risk Configuration is a crucial part of using Drova GRC to its maximum effect. This process commences with the set-up of Risk parameters on this tab. Changes made here will be evident ...Risk Hierarchy
In Risk Management, some Risks give rise to other Risks. Typically these Risks are high-level, an example being the occurrence of WHS incidents which introduces follow-on Risks such as: Employee absence, Deterioration of Company reputation, Financial ...Adding a Risk
Note: Create Risk record functionality is restricted to members of ‘Create Risk’, or an Administrator, System Security Group A Risk record can be created either from the Risks List page or the Risk page. Access the Risk Records list. From the ‘Risks’ ...Completing a Risk Review
When you complete a Risk Review, there are additional things you must do beyond reporting the date completed, by whom, adding comments and attaching supporting documentation. You must also: check any KRI Tasks linked to the Risk Review, check any ...The Risk Management Process
The following flowchart outlines the Drova Risk Management process. Note: The Risk Management features are highly configurable—you can use as much or as little of the Risk Management features set as your organisation needs. As such, this section ...